Neuron Tracing and Active Learning Environment (NeuroTrALE)
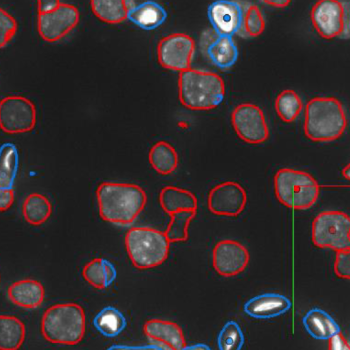
This open-source software enables researchers to create high-resolution maps (i.e., atlases) of the brain's network of neurons by applying artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to the evaluation of high-dimensional biomedical data. NeuroTrALE addresses a major challenge in AI-assisted brain mapping: a lack of labeled data for training AI systems to build atlases essential for study of the brain's neural structures and mechanisms.
Background
High-resolution, networked brain atlases that pinpoint differences between healthy and diseased brains can help improve scientists' understanding of the underlying mechanisms of many neurological disorders. These atlases can facilitate the development of drugs and treatments for conditions like Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, and epilepsy.
Thus, a top priority of the NIH's Brain Research Through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies initiative is creating atlases of the human brain at different scales with improved speed and accuracy. Despite advances in brain imaging, such mapping of the human brain on a cellular level is labor-intensive, and efforts to enable automated AI systems to build these maps have been limited by a lack of labeled data for training such systems.
NeuroTrALE
This software package streamlines data labeling for training AI algorithms to construct atlases essential for research into the brain’s functions. NeuroTrALE is designed as an end-to-end system that performs processing and annotation of dense microscopy data showing neuron localization and connectivity in multiple brain regions. NeuroTrALE integrates active machine learning techniques with current neuron segmentation and tracing algorithms to improve training with data labels. Through a web browser, domain experts can review the NeuroTrALE's high-dimensional atlases overlaid on the raw imagery; create and edit annotations; and review multiple annotated datasets at once.
Even though a number of neuroscientific software packages are available, many existing tools are workstation-based and limited to processing a few neurons at a time. Neuroglancer, Google's open-source, web-based bio-image viewer that served as a building block for NeuroTrALE, did not have an editing capability. With NeuroTrALE's added features, it is now the only tool that processes, reviews, annotates, and enables editing of dense microscopy data from multiple brain regions in a cloud-computing environment. After experts review results in NeuroTrALE, the labeled data are available for training machine learning models used to improve AI-generated brain atlases.
Benefits
- Allows automated data processing, image analysis, visualization, and editing via a web browser on a smart device
- Utilizes a cloud-based supercomputer to support the processing of brain datasets on the order of terabytes and petabytes
- Includes necessary libraries, frameworks, and dependencies for interfacing with any operating system equipped with correct runtime software
Potential Use Cases
- Study /understanding of the brain and its dynamics
- Development of therapeutics for cognitive disorders
Additional Resources
NeuroTrALE has been made available via an open-source license under Google’s Neuroglancer software: https://zenodo.org/record/5573294
"New open-source tool helps to detangle the brain," July 22, 2024
A. Michaleas et al., "Active Learning Pipeline for Brain Mapping in a High Performance Computing Environment," in Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE High Performance Extreme Computing Conference, Dec. 2020.
2024 R&D 100 Award winner