Optical Systems Test Facility
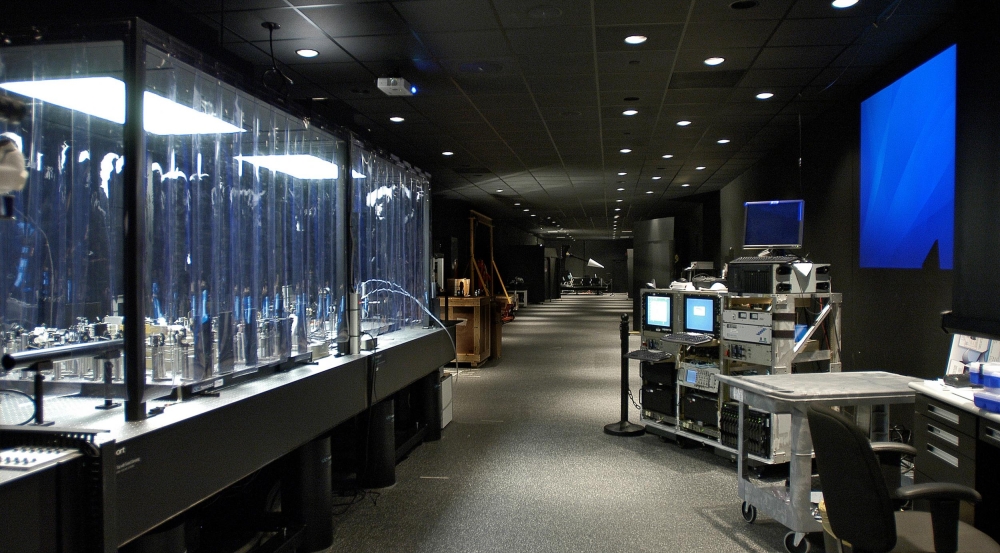

The Optical Systems Test Facility (OSTF) comprises four distinctive spaces used for developing and testing electro-optic systems. Each of these four facilities provides a specialized environment for the analysis and validation of diverse optical sensors. The OSTF's in-house infrastructure and resources support the Laboratory's role as a technology incubator. It is an ideal facility to test mature, preflight electro-optical sensor systems and to demonstrate the initial functionality of experimental prototypes.
Active Range
This section of the OSTF is a nearly 250-foot-long facility for developing and testing laser radar (ladar) sensors or other optical remote-sensing systems that require a long standoff distance with a laser transmitter/receiver pair. In the control room partitioned off from the actual test range, operators can perform analyses locally at workstations and remotely control higher-power laser systems. The range, painted black to be highly absorptive of stray light, features LED room lighting that lets researchers operate with the lights on and not damage sensitive infrared detectors. Independent heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and humidity controls that are largely shielded from building vibrations allow the space to remain at uniform environmental conditions. Staff can use an in-place laser radar framework, comprising a 1-meter collimating mirror and 50-meter free optical path with dynamic zoom and wavefront control, to emulate ranges significantly longer than the facility itself. At the far end of the facility is a dynamic target manipulator for controlling moving targets that are useful in testing coherent optical systems or inverse synthetic aperture ladar applications.
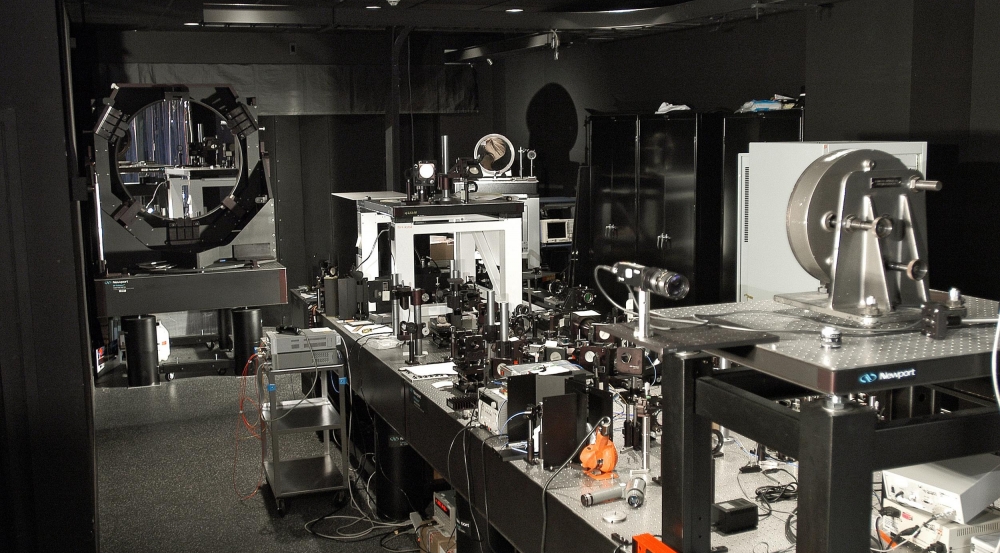
Passive Range
This range is designed for the evaluation of passive optical detectors and imaging systems. A large cryogenic chamber contains both the target and the unit under test on an optical breadboard. A resistive array and multispectral scene-projection optics can emulate the visible to longwave infrared (LWIR) scene that an imager under test might observe in a dynamic, operational scenario. This equipment is critical for testing how an imager or detector will perform in a high-altitude or space environment with low thermal background.
Optical Materials Measurements Range
Researchers use this range for analyzing materials and their properties as they are observed or sensed by optical systems. This facility features a suite of test apparatus capable of characterizing properties, such as radiance, reflectance, and polarization, in the spectra spanning from terahertz to LWIR. The researchers measure such properties to calculate the amount of light required to assure an optical system's communications link is uninterrupted and to understand the impact of different target materials on overall sensor performance.
Aerosol Imaging Test Bed
This facility is used in testing optical systems being developed to detect chemical or biological agents. In the test chamber, various chemical or biological agents can be aerosolized at controlled concentrations and rates. Researchers can evaluate a system's ability to detect particles of the agents that were introduced into the chamber.
