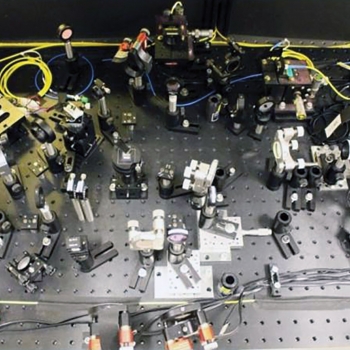
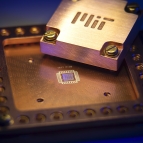
Quantum Network Test Bed
The strange features of nature described by quantum mechanics have the potential to enable powerful advances in technology. Quantum entanglement is a particularly strange phenomenon in which two quantum systems cannot be accurately described individually but must instead be described in reference to each other. When distributed across a network, these entangled states can act as a shared quantum reference between users, enabling a range of applications. They can be used to generate secure encryption keys, to optimally link distributed sensor arrays, and to serve as interconnects between quantum processor units.
Our research team is developing a quantum network test bed to demonstrate the distribution of quantum states at high rates with scalable connectivity. In collaboration with several groups at MIT, we are pursuing a phased development approach by which state-of-the-art quantum technologies are systematically incorporated into a test bed that will be used to investigate quantum networking system applications. The initial test bed channel consists of two 43-kilometer optical fibers connecting systems at the Laboratory to ones at MIT. This network will allow researchers to characterize and test advanced technology and new applications in a real-world environment.